Answer these simple questions and we will find you the BEST prices
Which type of solar quotes do you need?
It only takes 30 seconds
100% free with no obligation

Get up to 4 quotes from our selected suppliers by filling in only 1 form

Save money by comparing quotes and choosing the most competitive offer

Our service is 100% free and with no obligation
- Market-Inspector.co.uk
- Photocopiers
- Industrial Printers
Industrial Printers in the UK
The Best Industrial Printer Solutions for Your Business
Industrial printing typically involves applying ink to a surface of a product to add functional or aesthetic value. This is not to be confused with traditional wide format graphic printing, also known as industrial digital printing or large format printing, which is used principally for promotional purposes.
Industrial printers or photocopiers can print a range of products and have a variety of purposes. Applications of industrial printers range from:
Industrial printers can be an expensive investment, and many companies go for printer leasing, in order to optimise cash flow. Regardless of what financing solution you're after, Market Inspector can help you.
Simply fill in the contact form and you will receive up to four quotes on industrial printers from suppliers near you. This service is free and non-binding!

Regardless of your needs, there is an industrial printer solution that can:
However, the application of industrial printers is not limited to traditional ink and toner based printing; 3D printing is a fast growing segment and businesses are starting to see the benefits of using 3D printing in the early stages of their product development processes.
As industrial printer cost will vary significantly depending on the type of printer, you must first familiarise yourself with the practical applications of industrial printers as well as all benefits and disadvantages. These will be reviewed below.
Printing Superior Packaging
Printing the packaging for your product range is vital when trying to create a strong perception of value and reliability for your customers. This process is highly customisable and involves the preparation of goods for transport, warehousing, sale and end customer use.

Versioning and customisation of packaging now allows brands to make a more personalised product and improved engagement in local markets, see the Coca-Cola company’s “Share a Coke With…” campaign.

Protecting, preserving, transporting and selling are all critical aspects of product packaging and high quality results will reflect positively on the brand and will improve the initial perception of the packaged product.
Examples of packaging printing include:
Functional and Aesthetic Surface Printing
There are many ways to add value to a product and one cost effective approach is to add surface prints that can improve the product's aesthetic value. Printing decals and designs on product surfaces is a great way to communicate the brand and add creative value. Common applications include: airplane exteriors, printed glass, added wood finishes, decal printing on bicycles and printing designs on textiles.
Improving a brand's competitive advantage through surface painting is an attractive option as it tends to deliver a high return on investment. Industrial printers that are capable of surface printing will transcend design changes and will be adaptable to a variety of product types.
3D Printing and Product Development
With the ability to decentralise engineering design and prototyping, 3D printing (also known as additive manufacturing) has a significant potential when it comes to reducing the lead time and cost of producing an array of products.
With a growing list of applications in various industries, this form of industrial printers can support industrial designers during the prototyping stage of manufacturing. Additionally, it allows certain goods to be produced locally and enables engineers to print precision parts for their production apparatus, thus extending their lifetime and reducing costs.
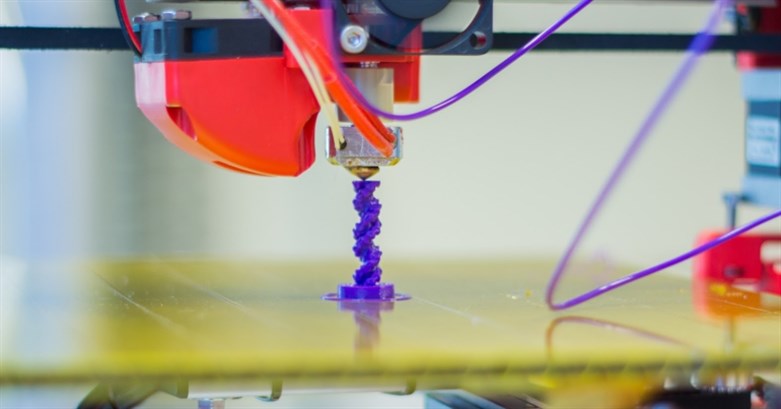

3D printing is infinitely customisable and is an attractive option for small scale manufacturers as it requires no retooling, only a change in the output from the software, lowers lead times, and provides unprecedented flexibility.
While the use of 3D industrial printers will incur a higher cost per printed unit, manufacturers will be able to attain a competitive advantage by offering added customisation without the added cost. This could be done either concurrently with traditional scaled production or exclusively, all depending on the required scale of production and the associated industrial printer costs.
Rapid prototyping can lead to reaching the market quickly at a low cost and with few errors. Doing so can be a challenge, but 3D printing can support engineers with the prototyping process by insourcing the development of the product where they can discover and eliminate errors early on in the process before investing in more expensive production processes.
In addition, 3D printers can produce injection moulds, living hinges and other mechanical parts in a variety of materials that can range in their hardness and durability.

Manufacturers could favour local production in situations where there is an immediate need for a part for the repair of their machinery. Alternatively, albeit a somewhat more advanced scenario, 3D printing could eliminate many complex elements of the modern supply chain in assembly processes by locally printing parts as opposed to having them delivered from distant production sites. While the per unit production cost may be higher, it will likely offset high transportation costs.
Barcode and Adhesive Label Printers
Supply chain optimisation within manufacturing, warehousing and distribution can drive down your long term industrial printer costs and improve the value that you deliver to your end customer. Doing so does not have to mean reimagining your supply chain or purchasing costly and complex IT systems.
Simple solutions such as investing in label making machines and thermal barcode industrial printers will have a high return on investment and their inherent simplicity will allow for painless internal compliance.

This can be achieved through a variety of ways:
RFID tags can be an accurate and reliable labeling solution for small and large supply chains alike. These reusable assets can improve transparency and allow management to monitor logistical efficiencies along the entire supply chain when passive read points are used. This helps improve the overall flow of the supply chain by providing data that can be used to determine bottleneck points and gauge the impact of improvements.
Functional Electronics Printing
Functional electronics printing (FEP) involves printing carbon based compounds onto a surface where it will run low performance applications. The very low cost industrial printer cost of FEP makes it an attractive solution for a wide array of applications, including the production of: RFID technologies, display panels, resistors and, solar cells.
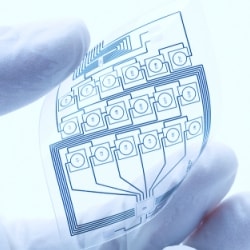
There are various benefits to printing low performance electronics, especially when compared to the traditional means of producing conventional electronics. The extremely low industrial printer prices, the ability to print on flexible substrates, the ability to print on large areas and the simplicity of the production process make functional electronics printing an advantageous alternative to traditional electronics manufacturing.
Find the Right Industrial Printer for Your Company
Industrial printers require a far more consideration and tailoring than standard business printers. It is important to have in-depth dialogue with a printer supplier to ensure all necessary features are included in your printer.
Complete a quote request form today and we will assist you with choosing an industrial printer or photocopier that meets your particular needs, for free. Our service team will connect you with qualified suppliers of high quality industrial printers that can support you and your supply chain operations.
Fill in the form in just 1 minute
We strive to connect our customers with the right product and supplier. Would you like to be part of Market Inspector?

