Answer these simple questions and we will find you the BEST prices
Which type of solar quotes do you need?
It only takes 30 seconds
100% free with no obligation

Get up to 4 quotes from our selected suppliers by filling in only 1 form

Save money by comparing quotes and choosing the most competitive offer

Our service is 100% free and with no obligation
- Market-Inspector.co.uk
- Vehicle Tracking
- Employee Rights & Laws
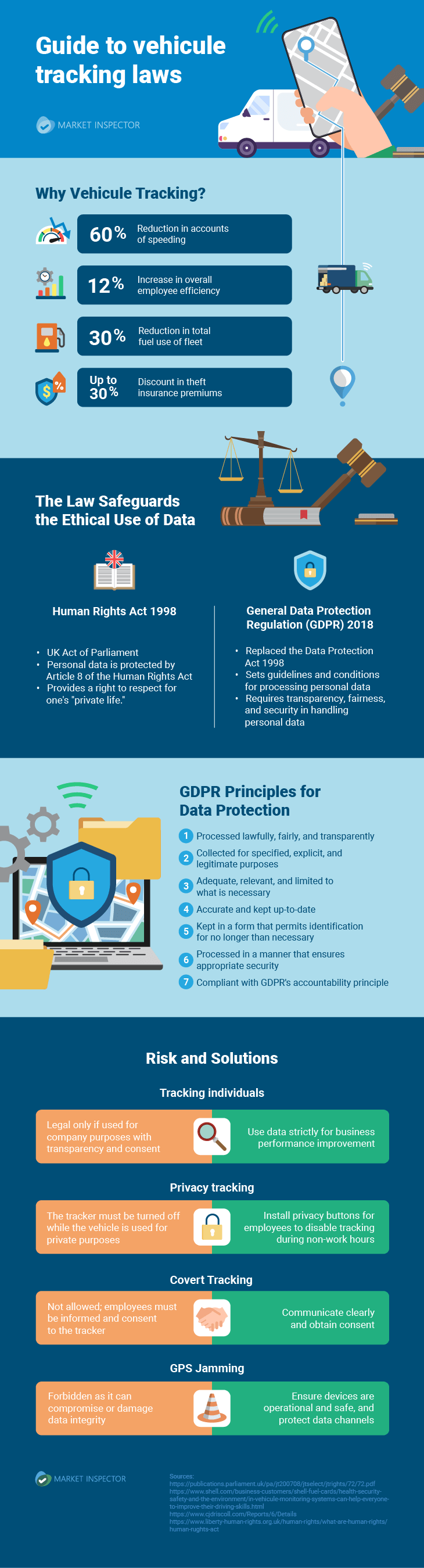
Vehicle Tracking: Employee Rights And Laws in 2024


- GPS tracking on company vehicles in the UK is legal if employers ensure transparency and GDPR compliance.
- GDPR requires businesses to handle GPS tracking data transparently, fairly, and securely. Employees must be informed about the trackers and data usage, and robust measures must be taken to prevent unauthorised access.
- Businesses must comply with the Human Rights Act 1998 and GDPR, ensuring tracking is for legitimate purposes, within work hours, and with employee consent. Violations can result in fines up to €20 million (approximately £16.9 million) or 4% of annual revenue.
In the UK, GPS tracking on company vehicles is legal, provided that employees are informed and have given their consent.
Vehicle tracking uses GPS technology to monitor vehicles' real-time location and status. It helps businesses enhance efficiency, improve safety, and reduce costs by providing detailed insights into vehicle movements and performance. It is commonly used in fleet management to ensure timely deliveries, optimise routes, and monitor driver behaviour.
Specific vehicle tracking laws have been established to protect employees and ensure personal data is not misused. These laws require transparency, consent, and adherence to data protection standards to balance operational needs with individual privacy rights.
- Describe your needs
- Get free quotes
- Choose the best offer
It only takes 30 seconds

GPS tracking laws in the UK

The legal framework for GPS tracking has evolved significantly in the UK, especially since the Data Protection Act 1998 was replaced by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in 2018. This change has brought more stringent requirements for businesses using vehicle tracking systems.
Under GDPR, businesses must ensure transparency, fairness, and security when handling personal data collected through GPS tracking.
Moreover, businesses must implement robust data protection measures to prevent unauthorised access, destruction, or damage to the data collected. This includes having clear policies and procedures for data handling, storage, and disposal. Data should be retained only as long as necessary for business purposes and then securely deleted.
The Human Rights Act also protects employees' privacy rights and requires that any monitoring be proportionate and necessary.
The Human Rights Act
The Human Rights Act 1998, incorporating the European Convention on Human Rights, mainly protects employees' privacy under Article 8. Respecting these rights requires compliance for businesses using GPS tracking systems.
- Necessity and proportionality: GPS tracking should be strictly for legitimate business purposes and limited to work hours. This ensures respect for employees' private lives and fosters a fair workplace.
- Consent: Businesses must obtain explicit, informed consent from employees before implementing tracking measures. This practice enhances trust and complies with legal standards.
- Data protection: Robust data security measures must be in place to protect collected data from unauthorised access and misuse. This ensures responsible data use and secure storage, aligning with legal requirements.
Prioritising these principles ensures compliance with the Human Rights Act and builds trust and transparency in the workplace.
UK GDPR 2018
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), introduced in 2018, replaced the Data Protection Act 1998, significantly changing data handling practices, especially for vehicle tracking systems.
We have listed the key GDPR provisions for vehicle tracking below.
- Fairness and transparency: Businesses must be open about the data they collect and its uses.
- Consent: Consent must be specific, informed, and freely given. The GDPR’s requirement for explicit consent departs from the more lenient standards under the Data Protection Act.
- Data minimisation: Only necessary data should be collected and used for the stated purposes. This principle helps prevent data misuse and ensures businesses do not overreach in data collection.
- Data security: Appropriate measures must be in place to protect data against unauthorised access, loss, or destruction. GDPR requires stricter accountability and documentation compared to the Data Protection Act.
- Accountability: Businesses must demonstrate compliance with data protection principles, maintain records of processing activities, and conduct data protection impact assessments (DPIAs) for high-risk activities like vehicle tracking.
- Individual rights: The GDPR enhances individuals' rights to access, correct, and delete their data, providing more control over personal information than the Data Protection Act.
Let’s compare the GDPR 2018 with the Data Protection Act 1998.
- Scope and clarity: GDPR offers more precise, more detailed guidelines on data processing, making compliance more straightforward to understand and implement than the more general provisions of the Data Protection Act.
- Consent requirements: The shift to explicit, informed consent under GDPR gives individuals greater control and understanding of data processing activities, a significant change from the broader consent previously acceptable.
- Accountability: GDPR requires detailed documentation and proactive measures to demonstrate compliance, whereas the Data Protection Act was less stringent in these areas.
- Enhanced individual rights: GDPR strengthens individuals' rights to data portability, erasure, and access, providing more robust protections than the Data Protection Act.
- Penalties: GDPR introduces stricter penalties for non-compliance, with fines up to €20 million (approximately £16.9 million) or 4% of annual global turnover, much higher than under the Data Protection Act.
By adhering to these GDPR provisions, businesses can ensure compliance, build trust with employees, and demonstrate a commitment to data protection.
What is allowed in business vehicle tracking?

When a company installs GPS tracking devices for fleet monitoring on its vehicles, it must respect employees' rights and fulfil legal obligations. Vehicle tracking can provide significant benefits, but strict rules govern its use. These guidelines apply to all business vehicle categories, including cars, vans, trucks, and motorcycles.
Risks and legal implications of vehicle tracking laws
Vehicle tracking systems offer significant benefits but have potential legal risks and implications that need careful management.
Potential risks
- Invasion of privacy: Using tracking data to monitor employee behaviour beyond work-related purposes can lead to privacy invasion claims, especially if tracking occurs outside of working hours or without proper employee consent.
- Non-compliance with GDPR: Failing to comply with GDPR can result in significant fines, including improper data collection, lack of transparency, and inadequate data security measures.
- Employee consent and awareness: Businesses could only face legal action with adequate employee consent and awareness. Consent must be explicit, informed, and documented.
- Data security breaches: Sensitive data from tracking devices must be protected against unauthorised access. Breaches can lead to legal penalties and damage to the company’s reputation.
Legal implications
- GDPR compliance: Ensure all personal data collected via vehicle tracking complies with GDPR.
- Human Rights Act: Employees have the right to privacy under the Human Rights Act. Misusing tracking data to monitor personal activities can violate this right and lead to legal action.
- Employment law: Using tracking data for disciplinary purposes without clear policies and employee consent can result in employment disputes and legal challenges.
Possible solutions for vehicle tracking risks
- Clear communication: Thoroughly communicate with all employees before implementing or changing vehicle tracking systems.
- Stay updated: Regularly review and update policies to ensure compliance with current laws and promptly implement necessary changes.
- Essential features: Ensure tracking devices have necessary features like a privacy button, allowing employees to disable tracking during non-work hours, and avoid using jamming devices
- Data protection: Implement robust data security measures to prevent leaks, misuse, or unauthorised access. Regular audits and data protection training can help maintain high-security standards.
By addressing these risks and adhering to legal requirements, businesses can use vehicle tracking systems effectively while protecting employee privacy and ensuring compliance.
Can a tracker be used as a timesheet?
A vehicle tracker can be used as a timesheet to monitor work hours, but it must comply with legal guidelines and respect employee rights.
Functionality
Vehicle trackers log data such as arrival and departure times, time spent at job sites, and total journey duration. This data can be used to generate timesheets, providing detailed records of employees' work hours and productivity.
Legal considerations
- GDPR compliance: Under GDPR, data collection must be fair and transparent. Employees should know what data is collected and how it will be used. Consent must be explicit and documented.
- Work hours only: Tracking should be limited to work hours. Using tracking devices outside these hours without consent can invade privacy and breach vehicle tracking laws.
- Data security: Protect collected data against unauthorised access. Ensure all data handling complies with GDPR standards to avoid breaches.
- Accurate timekeeping: Automated tracking provides precise records for payroll and compliance.
- Improved productivity: Real-time data allows better management of employee activities, optimises routes, and reduces downtime.
- Enhanced accountability: Employees are more likely to adhere to schedules, knowing their work hours are tracked accurately.
Using vehicle trackers as timesheets can be effective if operated within the legal framework, ensuring transparency, obtaining consent, and protecting employee data. This approach ensures compliance and promotes a trustworthy work environment.
Can a vehicle tracker be used in a disciplinary?
Yes, a vehicle tracker can be used in a disciplinary context, but strict legal guidelines must be followed to ensure compliance with UK laws and regulations.
- GDPR compliance: Follow the GDPR and Data Protection Act 2018 to ensure data is used lawfully, securely, and only for its intended purpose.
- Proportionality: Use tracking data proportionately and review its necessity regularly.
- Privacy: Limit tracking to work hours and work-related activities
Can you refuse to have a tracker on a company vehicle?
Employees generally have limited grounds to refuse the installation of a tracker on a company vehicle, especially if the tracking is conducted transparently and for legitimate business purposes.
- Legitimate business interests: Employers can track vehicles for efficiency, security, and policy compliance.
- Employee rights: Employees should be informed and consent to tracking, but refusal is problematic if it serves a legitimate purpose. Privacy rights must be respected .
- Data protection: Ensure tracking complies with GDPR, using data lawfully and securely
Tracking to check up on employees

It is entirely permissible for a company to monitor its business vehicles. However, there are stringent rules on how the collected data is used. The information from tracking devices must be used exclusively for legitimate management purposes, such as enhancing operational efficiency, ensuring vehicle safety, and overseeing adherence to company policies.
By adhering to the guidelines we mentioned earlier, such as privacy and data protection, companies can use vehicle tracking systems effectively for business management purposes while respecting employee privacy and following the law.
Tracking outside work hours
When business vehicles are used for personal activities by employees, it is acceptable to install GPS tracking devices in these vehicles. However, the GPS trackers must be deactivated during non-working hours to ensure employees' privacy is respected during their time.
Ensuring privacy
Companies can implement a privacy button on the tracking device to prevent privacy concerns. This feature allows employees to turn off data collection when off duty, ensuring they are not monitored during personal time.
By following these guidelines, employers can balance the need for vehicle tracking with respect for employee privacy, adhere to legal requirements, and foster trust within the workforce.
Can an employer track an employee without telling them?
No, an employer cannot track an employee without informing them. For legal and ethical considerations, employers must inform employees if a vehicle is being tracked and obtain explicit consent, explaining the purpose and data collected.
GPS-jamming
Using GPS-jamming devices is strictly forbidden. These devices can disrupt, alter, or otherwise compromise highly regulated data collection.
Legal regulations impose strict restrictions on any actions that could interfere with GPS data integrity, ensuring the protection and reliability of collected information.
Possible solutions for vehicle tracking risks
Navigating the legal implications of vehicle tracking can be challenging. To mitigate risks and ensure compliance with data protection laws, consider the following strategies:
- Thorough communication: Ensure that all employees are fully informed about using vehicle tracking devices. Discuss the placement, functionality, and purpose of the tracking system. Obtain their agreement before making any changes.
- Stay updated on regulations: Regularly review and stay informed about current laws and regulations related to vehicle tracking.
- Essential features: Ensure tracking devices include necessary features such as a privacy button. This allows employees to turn off tracking during personal time, thus protecting their privacy. Avoid using or allowing GPS-jamming devices, as these can compromise data integrity.
By following these guidelines, employers can effectively use vehicle tracking software systems while respecting employee privacy and adhering to legal requirements, thus minimising the risk of complaints and legal issues.
Compare multiple quotes
For UK business owners, it is essential to compare multiple quotes for vehicle tracking systems. Doing so unlocks the potential for significant savings and enhanced operational efficiency. Comparing quotes allows you to identify the best features, services, and prices tailored to your unique business needs.
Don't settle for the first offer you receive. Instead, explore various options to ensure you get the best deal available. This diligent approach can reveal differences in technology, customer support, and pricing that could substantially impact your bottom line.
Take the first step towards smarter business management by comparing multiple quotes for vehicle tracking systems today. Maximise your savings and operational efficiency now!
- Describe your needs
- Get free quotes
- Choose the best offer
It only takes 30 seconds

FAQ
Your employer can track your vehicle, but it must inform you about it and obtain your consent. The tracking should be limited to work-related activities and comply with data protection laws like GDPR.
Yes, it is legal for an employer to track an employee using GPS in the UK, provided the employee is aware of the tracking and has consented to it. The tracking must serve a legitimate business purpose and comply with data protection regulations like GDPR and the Data Protection Act 2018.
Yes, a vehicle tracker can be used in disciplinary actions in the UK. However, the employer must ensure transparency, obtain employee consent, and comply with GDPR. Tracking data should be proportionate and solely for the intended purpose of the disciplinary action.
Generally, you have limited grounds to refuse a tracker if it serves a legitimate business purpose. Employers must inform you and obtain your consent, but refusal is challenging if the tracking is necessary for business operations. Privacy rights and data protection laws must still be respected.

Nicole Bea Kerr is a content writer for Market Inspector, leveraging her experience in B2B journalism and editing. She is interested in bringing more awareness to sustainability and helping businesses make informed choices through insightful narratives.
We strive to connect our customers with the right product and supplier. Would you like to be part of Market Inspector?

